🌱 Comprehensive Guide to Indian Bamboo Farming: Complete State-Wise Details 🌱
🌿 Introduction to Bamboo Farming in India 🌿
Bamboo, known as the ‘green gold’, is a vital resource with significant environmental and economic potential across India. This guide covers detailed aspects of bamboo farming, tailored specifically to geographical suitability and Indian government policies.
📌 Bamboo Species Selection by Indian States
Different regions require different bamboo species based on climatic and geographical conditions:
- Assam: Bambusa tulda, Bambusa balcooa, Calamus rotang
- Nagaland: Dendrocalamus hamiltonii, Bambusa tulda, Teinostachyum dulloa
- Tripura: Melocanna baccifera, Bambusa tulda, Bambusa balcooa
- Manipur: Melocanna baccifera (dominant), Bambusa tulda, Bambusa balcooa
- Maharashtra: Dendrocalamus strictus, Bambusa bambos, Bambusa vulgaris
📌 Government Policies on Bamboo Farming
The Indian government promotes bamboo farming through the National Bamboo Mission (NBM), providing subsidies, training, and market linkages. State-specific policies:
- Assam: Focuses on biodiversity conservation, scientific harvesting, value addition, and industrial utilization to enhance livelihoods.
- Nagaland: Promotes bamboo as a renewable timber alternative, emphasizing ecological restoration, rural economic upliftment, and industrial development.
- Tripura: Encourages market-led community-based bamboo utilization, conservation, and industrial development.
- Manipur: Advocates sustainable bamboo development, climate resilience, and industrialization linked with rural employment.
- Maharashtra: Bamboo is declared as a priority sector, promoting bamboo clusters, industry linkages, and enhanced resource management.
For more details, visit: National Bamboo Mission
📌 Detailed Farming Guidelines
- Planting Method:
- Ideal spacing: 5m x 5m or 4m x 4m
- Bamboo per acre: Approximately 160-200 plants
- Water Requirement: Moderate (drip irrigation preferred)
- Submersible Pump: 5-7.5 HP suitable for efficient water management
- Growth Timeline & Costs:
- Time to mature: 3-5 years for initial harvest
- Cultivation cost: ₹40,000-₹60,000 per acre (initial setup)
- Farming cost per kg: ₹3-₹6
- Manpower required: 2-3 laborers per acre
📌 Bamboo Growth Monitoring & Measurement
Regular monitoring ensures quality:
- Diameter: Measure at chest height; optimal: 8-15 cm
- Internode Measurement: 20-40 cm standard; anomalies may indicate nutrient deficiency
- Annual Growth Rate:
- 1st year: 6-12 internodes
- 2nd year onwards: 10-15 internodes annually
| Year | Internodes per Culm |
| 1 | 6-12 |
| 2 | 10-15 |
| 3+ | 15-20 |
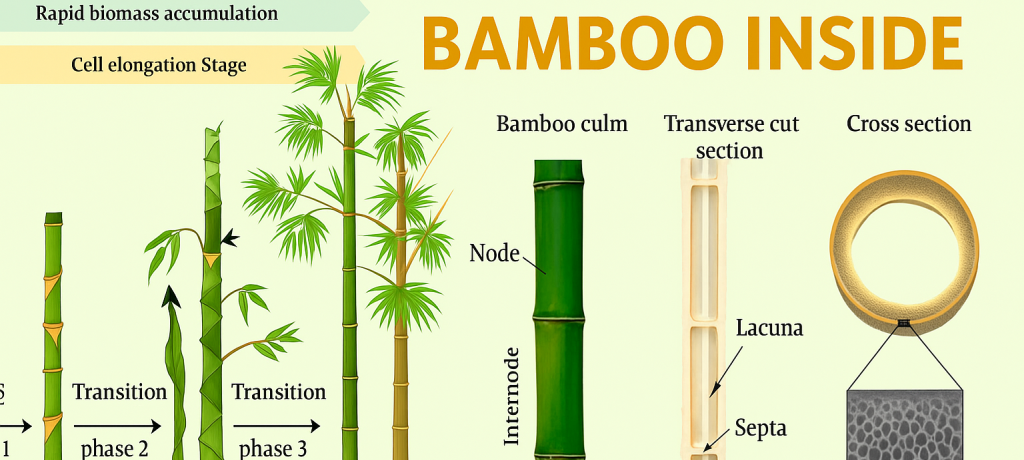
📌 Stages of Bamboo Growth
- Cell Division Stage: Initial phase of growth, critical for robust culm formation.
- Cell Elongation Stage: Rapid height increase and internode lengthening.
- Rapid Biomass Accumulation: Most biomass is accumulated, enhancing overall yield.

📌 Understanding Bamboo Structure
- Node: Solid joints connecting bamboo segments.
- Culm: Main bamboo stalk.
- New Culm: Newly emerging stalk from rhizome.
📌 Lifecycle & Replacement Culms
- Seeding Phase: Occurs every 40-60 years, marking end of bamboo lifecycle.
- Culm Replacement:
- 1st replacement: Year 3
- 2nd replacement: Year 5
- Equilibrium Genet Size: Typically 3-5 cm diameter at maturity
- Flowering Genet: Rare event, after decades, leads to mass seeding and plant death

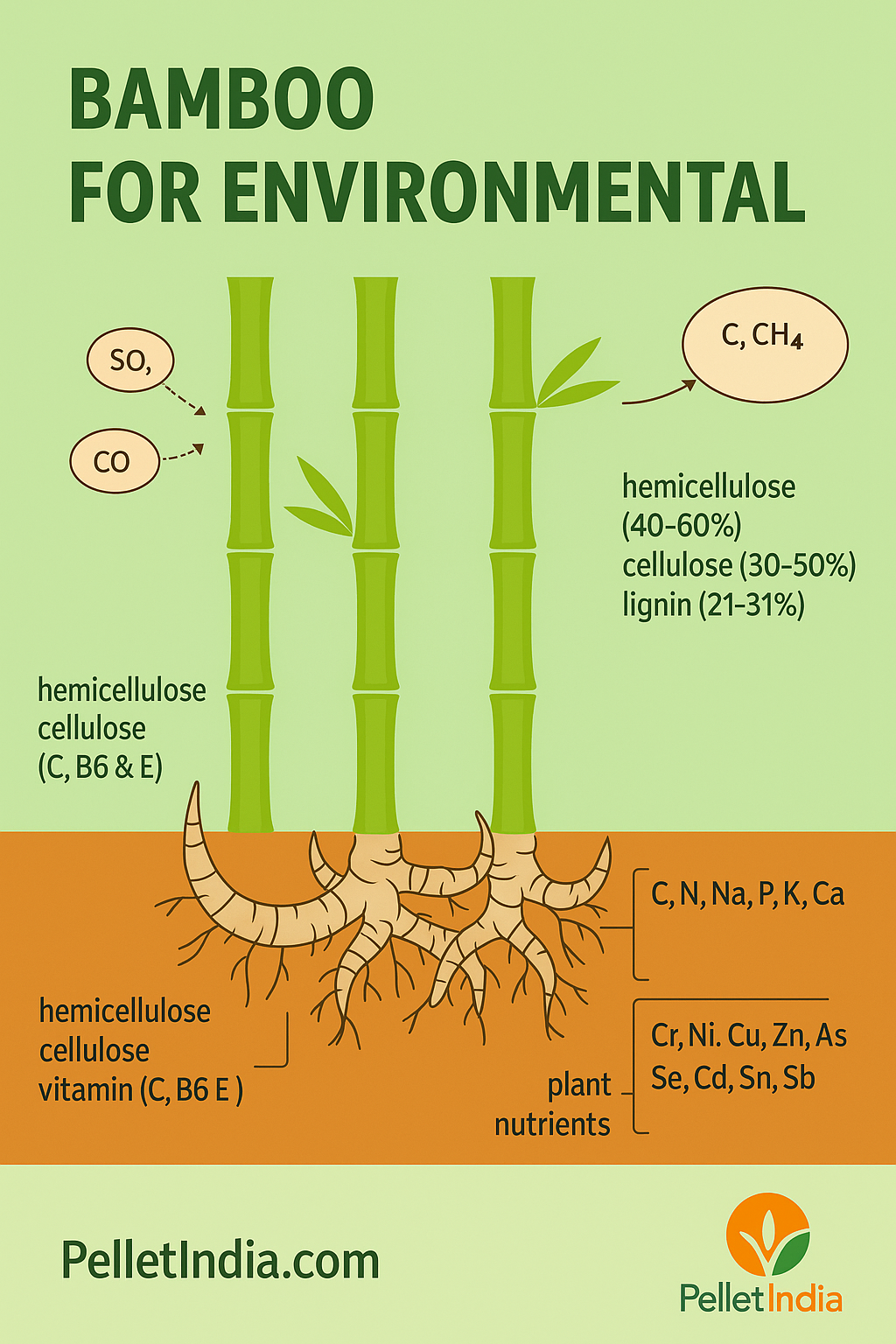
📌 Environmental Impact of Bamboo
- Reduces carbon footprint significantly
- Controls soil erosion, enhances groundwater recharge
- Serves as sustainable alternative to timber
📌 Bamboo Chips: Uses, Benefits, and Costs
- Uses: Biofuel, mulch, biomass energy
- Advantages: Renewable, high Gross Calorific Value (GCV): ~4,000 kcal/kg
- Estimated Costing (per kg):
- Farming: ₹3-₹6
- Processing: ₹2-₹4
- Labour & electricity: ₹1-₹3
- Total: ₹6-₹13
📌 Bamboo Pellets: Uses, Benefits, and Costs
- Uses: Bioenergy, industrial heating
- Advantages: Higher GCV: ~4,200-4,500 kcal/kg, low ash content
- Estimated Costing (per kg):
- Farming: ₹3-₹6
- Processing: ₹4-₹7
- Labour & electricity: ₹2-₹4
- Total: ₹9-₹17
🌍 Why Bamboo Can Save the World 🌍
- Fastest-growing renewable resource
- Carbon sequestration champion
- Supports biodiversity
- Essential in climate change mitigation
Disclaimer: This guide provides general understanding and may require additional, site-specific expert consultation for precise cultivation and economic planning.



📞 Contact Us for Biomass Solutions
📍 Servoday Plants & Equipments Limited
📞 +91 9427210483 | +91 9427210484
📧 sanjay@servoday.in
🌐 www.PelletIndia.com
👤 Contact Person: Sanjay Masuria
📲 WhatsApp: +91 9427210483
From Concept to Commissioning. We are with You.
Our policy is simple and transparent:
No undersized parts, no fraud, no fake components—genuinely serving since 1969. 🚀🔥